Big data and LASSO improve health insurance risk prediction
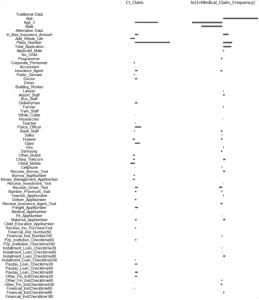
FAYETTEVILLE, GA, UNITED STATES, February 6, 2026 /EINPresswire.com/ -- A study in Risk Sciences examines whether alternative “big data” and the LASSO variable-selection method can strengthen health risk assessment in critical illness insurance. Using insurer application and claims records alongside smartphone-derived signals and public medical-claim information, the researchers report clear gains in out-of-sample predictive performance beyond traditional underwriting inputs. The paper also explores which categories of data may be most informative for underwriting.
Insurers must price and underwrite policies with incomplete information, while applicants often know more about their own health risks. This information gap can contribute to adverse selection and inefficient pricing. A new study published in Risk Sciences investigates whether alternative data sources (“big data”) and modern predictor-selection methods can improve health insurance risk assessment — which data sources are most worth collecting.
The researchers, from Peking University and University of International Business and Economics in China, analyzed proprietary critical illness insurance application and claim information from Chinese insurance company InsurTech. In addition to standard policy and demographic variables, the dataset includes applicant-authorized smartphone-related “label” information, such as device signals, location- and app-related indicators, and credit-inquiry related signals, as well as public medical-claim records from hospitals.
“To capture health risk, we used outcomes tied to critical illness claims as well as information derived from individuals’ prior public medical-claim history,” explains lead author Ruo Jia. “We found that adding big data and applying LASSO-style methods improves out-of-sample prediction compared with models relying only on traditional underwriting information.”
Notably, big data obtained from smartphone use offer extra-predictive power in addition to past medical histories.
“Because collecting and processing underwriting data can be expensive, we also applied Adaptive Group LASSO to identify which categories of variables are most useful,” says Jia. “We determined that the most fruitful data collection sources for health insurance underwriting are personal digital devices, recent travel experience, and insureds’ credit records.”
The authors emphasize that the analysis is predictive rather than causal: “we do not offer causal interpretations.” They also discuss limitations related to the study’ s coverage and context.
References
DOI
10.1016/j.risk.2025.100028
Original Source URL
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.risk.2025.100028
Funding Information
National Natural Science Foundation of China; National Social Science Foundation of China; Research Seed Fund of the School of Economics, Peking University
Lucy Wang
BioDesign Research
email us here
Legal Disclaimer:
EIN Presswire provides this news content "as is" without warranty of any kind. We do not accept any responsibility or liability for the accuracy, content, images, videos, licenses, completeness, legality, or reliability of the information contained in this article. If you have any complaints or copyright issues related to this article, kindly contact the author above.